 Direct foundation of the building takes place then, when the load is transferred to the bearing layer of the soil, located directly under the foundation.
Direct foundation of the building takes place then, when the load is transferred to the bearing layer of the soil, located directly under the foundation.
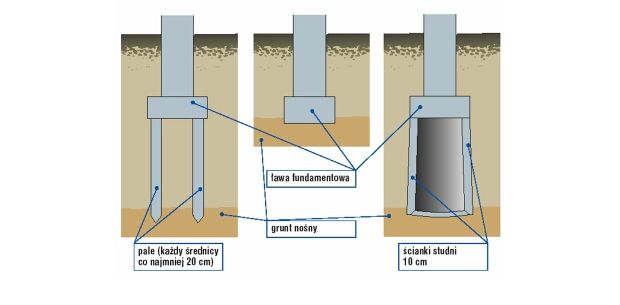
If the bearing layer of the ground is deeper than the foundation level of the building, you can use the so-called. indirect foundation, in which the load is transferred to the deeper bearing layer by means of additional structural elements such as piles or wells, placed in the ground.
• Micropiles – Reinforced concrete piles of small diameter, performed as drilled (diameter to 30 Cm), hammered, push-in or screw-in (diameter to 15 Cm); precast piles usually have a cross section of 25×25 cm do 40×40 cm and length to 18 m.
• Foundation piles drilled in the ground have a diameter of up to 2 m and a length of up to several dozen meters; concrete or reinforced concrete piles are most often used, which transmit the load to the ground through friction and pressure under the pile foot. Drilled piles are the latest solution, made by continuous pressure concreting (diameter CFA piles 40-150 Cm) and injection piles made by jet injection (so-called. jet-grouting).
• Wells – Concrete well rings filled with sand extend to the bearing layer.
Intermediate foundations should be made by specialized enterprises based on the design and construction calculations.